Depression and suicide are on the rise and more people are suffering from anxiety issues. IQ scores have dropped for all age groups and there is also a marijuana epidemic that is damaging young brains. There is a brain health crisis, and conventional therapy alone is not enough to deal with it. What people most often miss is the intimate connection between mental health and metabolic health.
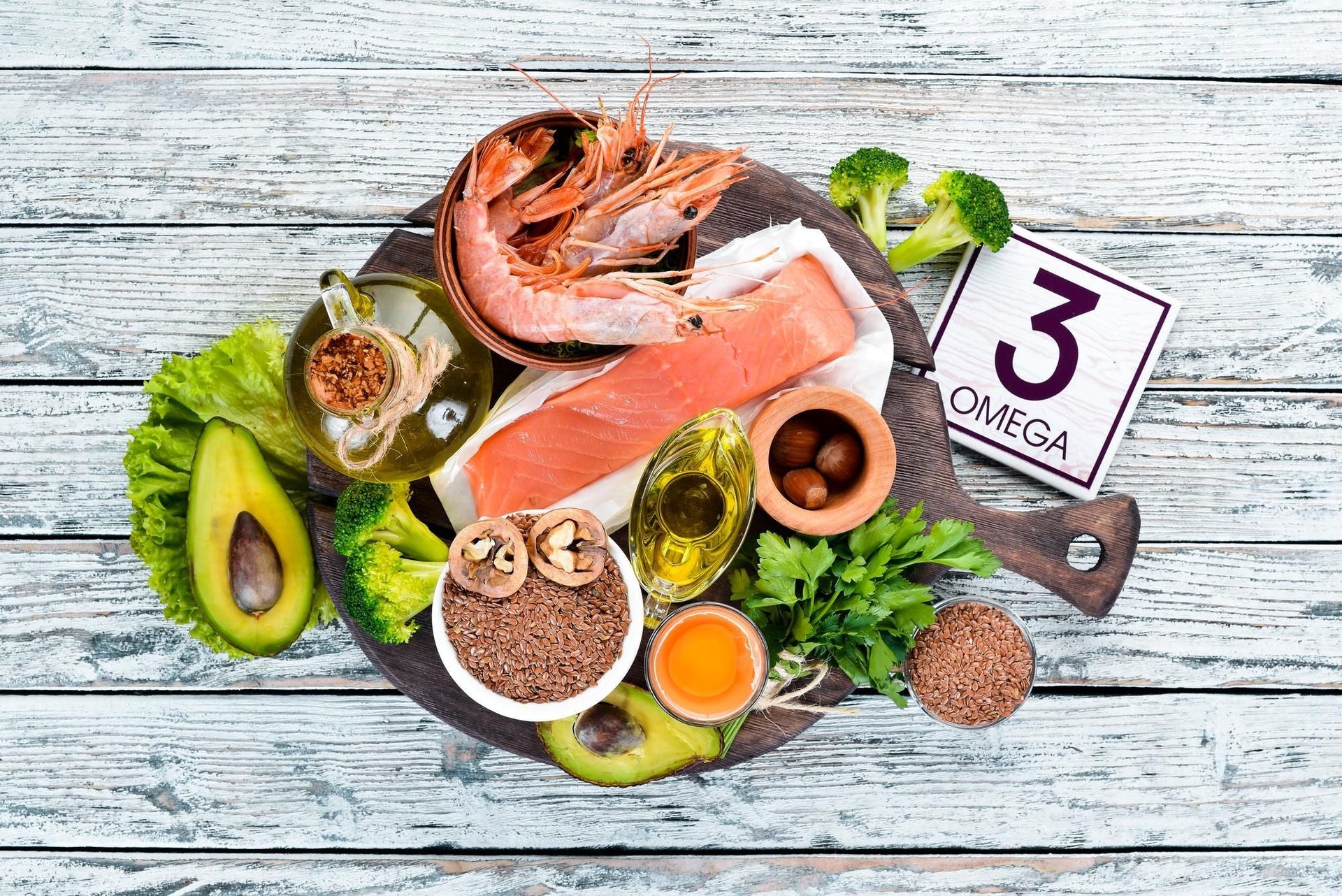
Omega-3 fatty acids are just one of the nutrients that have been found to be deficient in patients with anxiety, depression, alzheimers, ADHD, dementia and several other brain dysfunctions. When your cells are not getting the nourishment they need, your brain will struggle to remain healthy: Omega-3s are polyunsaturated fatty acids or the ‘good fats’ that are an essential fuel for your brain.
There are three main types of omega-3s: docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). Around 50-60% of our brain weight comes from lipids and omega-3 fatty acids contribute to 35% of it. DHA accounts for more than 40% of the total fatty acids in the brain. Humans have limited ability to synthesize DHA and EPA so diet becomes our main source to acquire it.
Sea foods such as fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, tuna, herring, and sardines contain high amounts of EPA/DHA. Veg sources of omega-3 include flaxseed, chia seeds and walnuts. Supplementing with krill oil or high-quality cod liver oil can also help you acquire optimal omega-3 levels.
While EPA plays a crucial role in controlling cellular inflammation, our brains are the most abundant in DHA in cell membranes which makes it crucial for nerve cell structure and function. Let’s look at some reasons why your brain loves omega-3s!
Cell membrane fluidity
When omega-3s enter the cell membranes they influence membrane fluidity and deformability. Cell membrane fluidity describes the freedom of movement of proteins and lipids within the cell membrane. Lack of omega-3s in the diet can lead to decreased membrane fluidity and in turn impair enzyme functions and contribute to inflammation and other health problems.
Omega-3s and neurotransmitters
Omega-3s can positively influence mental health by interacting with neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine and endorphins.
- Serotonin is the neurotransmitter that mediates satisfaction, happiness and optimism. By increasing serotonin levels, omega-3s may help in fighting depressive symptoms. While the exact pathway of how it affects serotonin is not known, some studies suggest omega-3s look after the release, uptake and binding of serotonin in the brain.
- People deficient in omega-3s often have low dopamine levels that are not just responsible for your motivation, pleasure and reward but also healthy cognitive functions such as working memory. Omega-3s impact the release and receptor function of dopamine and enhance the transmission of dopamine signals. This can be useful to treat conditions such as Parkinson's disease, ADHD and addiction.
- Endorphins are natural pain-relieving and mood-elevating hormones. Omega-3s can boost the release of endorphins that evoke euphoric feelings and better mood.
Hippocampal neurogenesis
There are two ways in which omega-3s can influence neurogenesis i.e. the process by which new neurons are formed in the brain. One, we spoke about omega-3s entering cell membranes and moderating fluidity. Fluidity affects neurogenesis through influencing signaling within cells and binding of neurotransmitters like serotonin to cell membranes.
Two, omega-3s like EPA restrict the release of inflammatory cytokines — small proteins that are activated as an immune response against pathogens. Recent studies have shown that these inflammatory cytokines affect neurogenesis by disrupting cell signaling and the blood brain barrier. Omega-3s combat chronic exposure to these cytokines that are factors in promoting mental disorders like Alzheimer’s and depression.
Better blood circulation
Omega-3s lead to increased blood flow in regions in the brain responsible for memory and cognition. While the exact mechanism is not known, it is mostly due to the improved functioning of endothelial cells that line our blood vessels and regulate blood flow. Better blood circulation may slow down cognitive aging and help combat early memory and learning deficiencies.
Synaptic plasticity
Omega-3s are known to increase the levels of several signaling factors involved in synaptic plasticity. Synapses are points at which a nerve impulse passes from one neuron to another. Synaptic plasticity is the ability of these synapses to strengthen or weaken over time. Omega-3s increase these synapses as well as the dendritic spines that collect electric impulses from other neurons. This enhances learning and memory, brain development, sensorial training, and recovery from brain lesions.
Stop neuronal cell death
Studies have shown that omega-3s in the diet can help balance levels of zinc in the brain and prevent cell death. DHA, specifically, reduces zinc uptake by cells that in turn reduces apoptotic cell death. This can help fight neurodegenerative disorders that may be influenced by zinc fluxes.
Larger brain volume
New evidence links a diet higher in Omega-3s to increased brain volume in women. A study assessed levels of EPA and DHA in more than a 1000 women. After 8 years, they conducted brain scans on these same women who on average reached the age of 78. They found that women who had higher levels of omega-3s displayed a larger total brain volume. They also displayed a 2.7% larger hippocampal volume - the region of the brain that controls memory. Hence, omega-3s can be useful to reduce neurodegeneration in patients with Alzheimer’s who witness a decline in their hippocampus.
Takeway
Fats have gotten a bad reputation for a reason, the modern diet is filled with saturated fatty acids and trans fatty acids while the consumption of omega-3s has decreased. This is just one nutrient that has immense benefits for the brain and can help treat mental health issues. Remember, out of all the omega-3s, DHA is the one that we are biologically primed for.
You don’t just have to toss aside your stress and worries, you can alter your reaction to them by giving your brain what it needs and keeping it healthy. If you or someone you know is suffering from mental health issues, a functional nutrition approach along with therapy can do wonders. Once people wake up to the importance of metabolic health for mental health, it can truly revolutionalise psychiatry.
REFERENCES
- Effects of fatty acid unsaturation numbers on membrane fluidity and α-secretase-dependent amyloid precursor protein processing
- Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Brain Functions: A Systematic Review
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Neurotransmitters: Unveiling the Impact on Serotonin, Dopamine, and Endorphins
- DHA: Powerful Omega-3 for Heart and Brain Health
- Omega-3 fatty acids upregulate adult neurogenesis
- Inflammatory Cytokines in Depression: Neurobiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
- New study demonstrates omega-3 fatty acids increase blood flow to regions of the brain associated with cognition
- Self-Reported Omega-3 Supplement Use Moderates the Association between Age and Exercising Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity in Older Adults
- The omega-3 fatty acid, DHA, decreases neuronal cell death in association with altered zinc transport
- Higher RBC EPA + DHA corresponds with larger total brain and hippocampal volumes